
Men are more likely to have uncontrolled high blood pressure than women. There has been no change in the prevalence of uncontrolled high blood pressure since 2011–12 (ABS 2018a).
11% whose blood pressure was controlled using medication/s ( Table S1 ). 23% with uncontrolled high blood pressure and. 

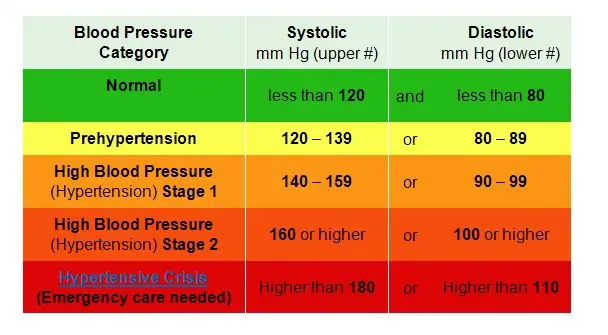
Who has high blood pressure?īased on measured data from the 2017–18 Australian Bureau of Statistics National Health Survey, about 1 in 3 people aged 18 and over (34%) have high blood pressure. Controlled blood pressure refers to those people who are taking blood pressure medication and have a normal blood pressure reading. 'Uncontrolled high blood pressure' is defined as measured systolic blood pressure of 140 mmHg or more, or diastolic blood pressure of 90 mmHg or more, whether or not they were taking blood pressure medication (ABS 2018).
The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) National Health Survey 2017–18 measured blood pressure at the time of the interview, and the definitions listed above were used in defining high blood pressure in the results presented here.
receiving medication for high blood pressure (Whitworth 2003). diastolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 90 mmHg, or. systolic blood pressure greater than or equal to 140 mmHg, or. The World Health Organization defines high blood pressure as including any of the following: High blood pressure can be controlled with lifestyle measures and medication, reducing the risk of developing chronic conditions.īox 1: How is high blood pressure measured?īlood pressure is the force exerted by the blood on the walls of the arteries and is written as systolic/diastolic (e.g. In addition to high salt intake, other risk factors for high blood pressure include poor diet, obesity, excessive alcohol consumption and insufficient physical activity. The ABDS 2015 estimated how much impact a diet high in sodium had on blood pressure levels in Australia using a risk factor causing a risk factor approach. About 21% of high blood pressure burden in Australia in 2015 is due to a diet high in sodium-higher for men (23%) than women (17%)-based on unpublished estimates from the Australian Burden of Disease Study (ABDS) (see Burden of disease). In 2015, 5.8% of the total burden of disease in Australia was due to high blood pressure (AIHW 2019). High blood pressure-also known as hypertension-is a major risk factor for chronic conditions including stroke, coronary heart disease, heart failure and chronic kidney disease (see heart stroke and vascular disease and chronic kidney disease for more information).








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
